Chapter – 5.3 Laxative
Topic: Aloe
ALOE
Aloe Vera is a plant species of the aloe genus. If grows widely in tropical climate and is also cultivated due to its agricultural and medicinal values.
Synonym: Aloe, Alovera, Guarpatha
Biological Source: It consist of dried juice of leaves of Aloe barbadensis Miller and Aloe Africana.
Family: Liliaceae.
Geographical Source: Most of the species of aloe are indigenous to Africa. But now introduced into West Indies and Europe.
Preparation: Various methods are used to prepare aloes commercially in Africa, as well as in west indies. Following is the general method of preparation.
• The leaves are transversely cut at the base and the incised ends placed downwards in a ‘V’ shaped trough having a hole at its bottom. The latex is evaporated in a kettle made of copper where it gets solidified. When the latex is concentrated gradually and then cooled slowly, it gives rise to an opaque product. The aloe thus obtained is termed as ‘hepatic’ or ‘livery’ aloe. • If the latex is concentrated rapidly, followed by sudden cooling the resulting product appears to be transparent and relatively brittle in nature. The broken surface has a glassy surface. Such a product is commonly known as ‘lucid’ or ‘glassy’ aloe.
Morphological Characters:

Colour: Depends upon variety from which it is obtained. It is Green to dark brownish black in colour.
Odour: Characteristic
Taste: Bitter taste
Size: It is available in various sizes.
Solubility: It is entirely soluble in 60% alcohol and it partially soluble in water.
Chemical Constituents: All variety of aloes a yellow coloured crystalline substance known as barbloin (c-glycoside), resin & aloe – emodin. Isobarbalion is present in curacao and cape aloes. Cap aloes are characterized by the presence of an amorphous compound β-barbalion, aloinosides A & B.
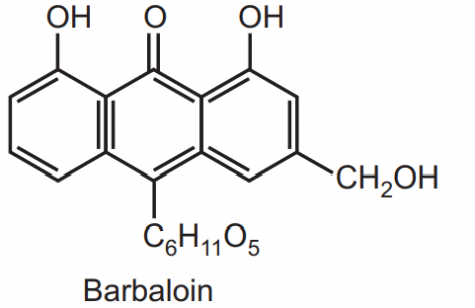
Identification Test:
1. Borax Test: To 5 ml of the above test solution add 0.2 gm of pure borax and heat gently till it gets dissolved. Transfer a few drops of the resulting solution into a test tube filled with distilled water, the appearance of a green colored fluorescence due to the formation of aloe emodin anthranol shows its presence.
2. Bromine Test: When equal volumes of the test solution and bromine solution are mixed together, it yields a pale-yellow precipitate due to the production of tetrabromaloin.
3. Nitric Acid Test: The Test solution of aloes when made to react with nitric acid, it gives Deep brownish red to pale brownish yellow.
4. Cupraloin Test: To 10 ml of a 0.4% (w/v) aqueous solution of aloe add a drop of the saturated solution of copper sulphate, immediately followed by 1gm of NaCl and 20 drops of ethanol (90% v/v). It produces a wine red colour lasting for few hours.
Uses:
1. Though, both aloes and aloin are official drugs, mostly used as a purgative by exerting its action mainly on colon.
2. Aloes find its usefulness as an external aid to painful inflammatory action.
3. It constitutes an important ingredient in the ‘Compound Tincture of Benzoin’ (or Friar’s Balsam).
4. Aloe gel are used in the treatment and cure of radiation burns or sun burn to get immediate relief from itching and pains.
5. As a hair tonic.
6. It stimulates the growth of hairs.
7. It is also used in acne, pimples etc.
8. It is also used as a moisturizers.